Jun. 26, 2015 Press Release Physics / Astronomy
The quantum spin Hall effect is a fundamental property of light
In a paper that crystalizes knowledge from a variety of experiments and theoretical developments, scientists from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) in Japan have demonstrated that the quantum spin Hall effect—an effect known to take place in solid state physics—is also an intrinsic property of light.
Photons have neither mass nor charge, and so behave very differently from their massive counterparts, but they do share a property, called spin, which results in remarkable geometric and topological phenomena. The spin—a measure of the intrinsic angular momentum—can be thought of as an equivalent of the spin of a top. In the research published in Science, the team found that photons share with electrons a property related to spin—the quantum spin Hall effect.
"We had previously done work looking at evanescent electromagnetic waves," says Konstantin Bliokh, who led the research, "and we realized the remarkable properties we found, an unusual transverse spin—was a manifestation of the fact that free-space light exhibits an intrinsic quantum spin Hall effect, meaning that evanescent waves with opposite spins will travel in opposite directions along an interface between two media." Evanescent waves propagate along the surface of materials, such as metals, at the interface with a vacuum, in the same way that ocean waves emerge at the interface between the air and the water, and they decay exponentially as they move away from the interface.
The quantum spin Hall effect for electrons allows for the existence of an unusual type of material—called a topological insulator—which conducts electricity on the surface but not through the bulk of the material. The team was intrigued to learn that an analogy for these can be found for photons. Though light does not propagate through metals, it is known that it can propagate along interfaces between a metal and vacuum, in the form of so-called surface plasmons involving evanescent light waves. The group was able to show that the unusual transverse spin they found in evanescent waves was actually caused by the intrinsic quantum Hall effect of photons, and their findings also explain recent experiments that have shown spin-controlled unidirectional propagation of surface optical modes.
Bliokh continues, "On a purely scientific level, this research deepens our understanding of the classical theory of light waves developed by James Clark Maxwell 150 years ago, and it could also lead to applications using optical devices that are based on the direction of spin."
Franco Nori, group director of the CEMS Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group and team leader of the Interdisciplinary Condensed Matter Physics Team in the Interdisciplinary Theoretical Science Research Group (iTHES), who organized the project, says, "This work was made possible by the interdisciplinary nature of RIKEN, as we were able to bring together discoveries made in several different areas, to show that transverse spin, locked to the direction of propagation of waves, seems to be a universal feature of surface waves, even when they are of different nature."
Reference
- Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, and Franco Nori, Quantum spin Hall effect of light, Science (2015), 10.1126/science.aaa9519
Contact
Group Director
Franco Nori
Research Scientist
Konstantin Y. Bliokh
Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group
Quantum Information Electronics Division
RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science
Team Leader
Franco Nori
Interdisciplinary Condensed Matter Physics Team
Interdisciplinary Theoretical Science Research Group
Research Groups
Jens Wilkinson
RIKEN Global Relations and Research Coordination Office
Tel: +81-(0)48-462-1225 / Fax: +81-(0)48-463-3687
Email: pr@riken.jp
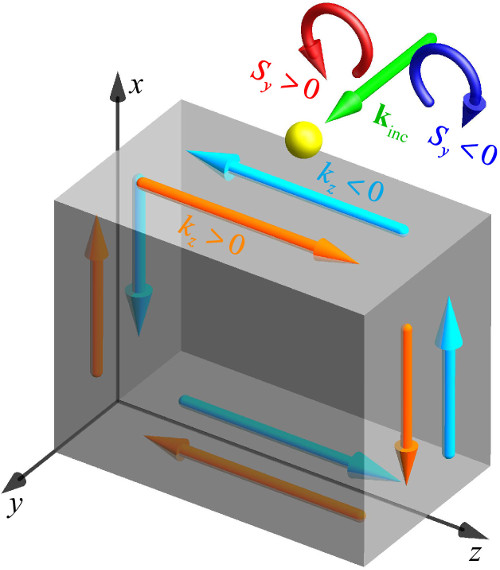
Schematic of experiments demonstrating the quantum spin Hall effect of light
