Dec. 1, 2017 Press Release Physics / Astronomy
Monopole current offers way to control magnets
In work published in Physical Review Letters, scientists from RIKEN in Japan have discovered interesting new magnetic properties of a type of materials known as “quantum spin ice.” These materials demonstrate interesting properties as they behave as “frustrated magnets”—systems that can settle into various magnetic states because of their special geometry. One important property of these materials is that they have virtual monopoles—particles that are either north or south but not like typical magnets, which invariably have both a north and south pole confined together.
Using numerical simulations, the group showed how a magnetic field could be used to control the properties of north and south poles, which are fractionalized from magnetic moments of electrons, on a frustrated magnet called a quantum spin ice.
The group first proposed a model for quantum spin ice—spin ice based on quantum properties—in 2010 in order to describe the low-energy magnetic properties of magnetic rare-earth pyrochlores—a type of mineral that show interesting physical properties. In 2012, experiments showed that this model was valid. This system includes a quantum spin liquid state where spins—the property of electrons that lead to magnetic properties—are prevented from ordering and freezing by zero-point motion, a type of motion allowed even at zero temperature under quantum mechanics, of their monopoles. Since monopole charges are subject to a conservation law, the motion of north and south poles directly affects the direction of magnetic moments in the system. In addition, electric charges are not carried by these monopoles, and thus the monopole current is not accompanied by an electric current that would lead to a large energy loss through Joule heat. “Because of this,” says Shigeki Onoda, the leader of the group, “monopole current offers a potentially efficient way of controlling magnets without loss.”
Through this work, the researchers revealed that there are successive transitions from the quantum spin liquid state if a magnetic field is applied in a special direction along which kagome-lattice layers and triangular-lattice layers are stacked one on top of the other. First, the magnetization of the system rises smoothly to a value two-third of the maximum value in the quantum spin liquid state, and then remains at that level in a finite range of the field strength, which is called the 2/3 magnetization plateau. In this plateau state, the zero-point motion of monopoles are spatially confined and localized, and thus this state cannot host a coherent monopole current. However, as the strength of the magnetic field is increased, the magnetization of the material eventually begins to rise again and concomitantly, the monopole charges become disproportionate and show a superfluidity. This is a magnetic analogue of a supersolid in helium 4, where the atoms show both a non-uniform spatial distribution and a superfluidity, which supports frictionless and thus dissipationless current, at extremely low temperature. The monopole supersolid phase survives until the magnetization saturates to the maximum value.
According to Onoda, “Our work indicates that the conductivity associated with the monopole current can be substantially controlled by applying a magnetic field to quantum spin ice and that it is possible to host dissipationless monopole current in the monopole supersolid phase. Our findings may also open a novel route to the efficient control of magnetism for a range of potential applications such as memory devices.”
The paper was published online on November 13. The work was partially supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research under Grant No. 24740253 and No. 16K05426 from Japan Society for the promotion of Science and under Grant No. 15H01025 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, and Technology of Japan and by the RIKEN iTHES project. Numerical computations were performed using the HOKUSAI-Great Wave supercomputing system at RIKEN.
Reference
- Troels Arnfred Bojesen and Shigeki Onoda, Quantum spin ice under a [111] magnetic field: from pyrochlore to kagome, Physical Review Letters (2017), doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.227204
Contact
Senior Research Scientist
Shigeki Onoda
Condensed Matter Theory Laboratory
Chief Scientist Laboratories
Jens Wilkinson
RIKEN International Affairs Division
Tel: +81-(0)48-462-1225 / Fax: +81-(0)48-463-3687
Email: pr@riken.jp
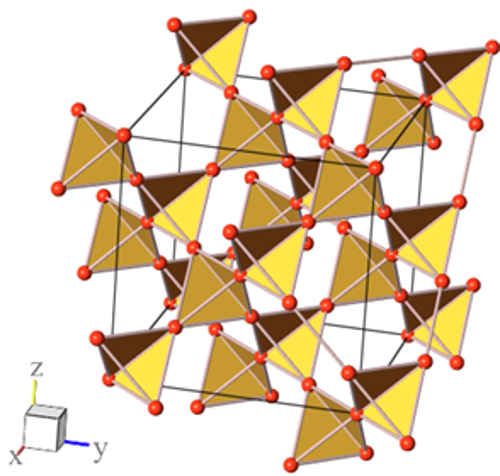
Pyrochlore lattice structure
![Figure showing phase diagram and of quantum spin ice under the [111] magnetic field](/medialibrary/riken/pr/press/2017/20171201_2/fig2-500.png)
Phase diagram and of quantum spin ice under the [111] magnetic field
