Jun. 8, 2012 Research Highlight Biology
Revealing a pollutant’s Achilles’ heel
Recent elucidation of the structural architecture of a bacterial enzyme involved in microbial denitrification could help to reduce its harmful effects
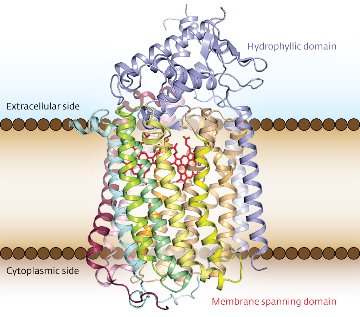 Figure 1: The structure of G. stearothermophilus qNOR, with the transmembrane portion visible between the brown lines. Reproduced from Ref. 1 © 2012 Yushi Matsumoto et al.
Figure 1: The structure of G. stearothermophilus qNOR, with the transmembrane portion visible between the brown lines. Reproduced from Ref. 1 © 2012 Yushi Matsumoto et al.
Nitric oxide (NO) is a versatile free radical that plays central roles in the environment as well as living organisms. At low concentration in the human body, for example, NO protects organs against pathogens by acting as a chemical weapon. Bacteria counter this response with respiratory enzymes called nitric oxide reductases (NORs) that effectively neutralize NO. By solving the crystal structure of the quinol-dependent reductase (qNOR) from the bacterium Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Fig. 1), a research team in Japan led by Yoshitsugu Shiro from the RIKEN SPring-8 Center, Harima, has provided insight into this microbial denitrification process1.
In previous investigations of reductases, biologists had limited their focus to the enzyme called cytochrome c-dependent NOR (cNOR), despite the greater abundance of qNOR in macro-organisms. This is because cNOR exhibits similar amino acid sequences and metal ligands to other respiratory enzymes known as cytochrome oxidases.
To elucidate the molecular evolution of these respiratory enzymes, and to understand how this evolution affects enzymatic function, Shiro and his team compared the newly determined three-dimensional structure of qNOR to those of cNOR and the cytochrome oxidases. They discovered that the overall structures of the reductases were identical and the portions of qNOR and cNOR that span cell membranes matched those of the oxidases. However, qNOR lacked the iron-containing functional group, heme c, which provides electrons to cNOR. Unexpectedly, this domain maintained an analogous folding pattern to that of cNOR, thanks to bulky residues that compensate for the void created by the absence of heme c.
By identifying key structural components of qNOR, Shiro and colleagues revealed the mechanism of this enzyme: the electron-donating quinol molecule interacts with the transmembrane portion of qNOR through hydrogen bonds, facilitating electron transfer to it. In addition, the crystallographic data showed that this transmembrane domain enclosed water molecules that formed a hydrophilic channel extending to the cytoplasm. Computer-aided simulations indicated that this channel could transport catalytic protons to the reaction center where NO reduction takes place. “The water channel of qNOR is located in the same region as the proton channel of oxidases—[this helps explain] how respiratory enzymes acquired their proton-pumping ability,” adds Shiro.
The researchers are currently investigating compounds that can interact with qNOR and cNOR. “In the near future, we plan to characterize the structure and function of bacterial NOR–inhibitor complexes,” says Shiro. These inhibitors could be harnessed to reduce global nitrous oxide emissions or used in antibacterial drug design.
References
- 1. Matsumoto, Y., Tosha, T., Pisliakov, A.V., Hino, T., Sugimoto, H., Nagano, S., Sugita, Y. & Shiro, Y. Crystal structure of quinol-dependent nitric oxide reductase fromGeobacillus stearothermophilus. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 19, 238–245 (2012). doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2213
