Aug. 10, 2021 Research Highlight Biology
Unexpected diversity in virus-derived sequences in the human genome
Powerful genetic analysis tools reveal that people exhibit a surprising level of variation in virus-derived genetic sequences
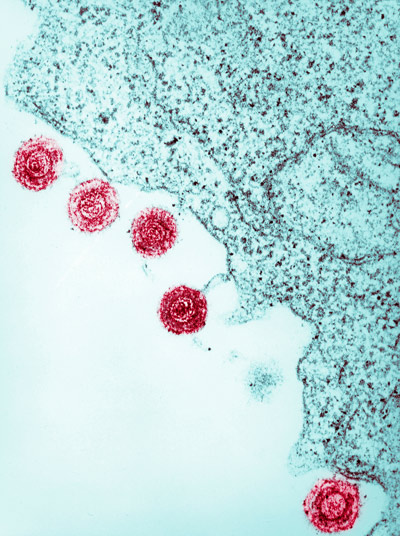 Figure 1: A false-colored electron micrograph showing human herpesviruses 6 (HHV6; red circles) infecting a cell. RIKEN researchers have discovered new heritable structural variants derived from HHV6 in human genomes. © CALLISTA IMAGES/CULTURA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Figure 1: A false-colored electron micrograph showing human herpesviruses 6 (HHV6; red circles) infecting a cell. RIKEN researchers have discovered new heritable structural variants derived from HHV6 in human genomes. © CALLISTA IMAGES/CULTURA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Three RIKEN geneticists have discovered previously undetected snippets of genetic material from viruses lurking in our DNA1. The methods they developed for this discovery will be valuable for determining when this viral genetic material entered the human genome and also whether it can give rise to differences between individuals.
Roughly 8% of the human genome can be traced backed to retroviruses—viruses that reverse the normal order of genetic transcription, having an RNA genome that is reverse-transcribed into DNA and then inserted into the genome of the host cell. The most infamous retrovirus is the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
While retroviruses can have devastating effects on human health, the viral genetic material inserted in our genomes can provide useful functions. For example, retroviral proteins expressed in the placenta enable humans and other mammals to give birth to live offspring rather than eggs.
“During the course of human evolution our ancestors acquired many virus-derived sequences, some of which impart useful functions,” says Shohei Kojima of the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS). “I used to think that viruses were menaces, but some of their genetic sequences are essential for human development.”
Over the last two decades, researchers have discovered much about the retroviral genetic sequences in the human genome, as well as viral-origin sequences derived from non-retroviruses. But it is unclear how much these sequences vary between people and whether variants could give rise to different human characteristics.
 Shohei Kojima and two RIKEN co-workers have discovered a surprisingly high level of variation between people in human endogenous viruses. © 2021 RIKEN
Shohei Kojima and two RIKEN co-workers have discovered a surprisingly high level of variation between people in human endogenous viruses. © 2021 RIKEN
Now, Kojima, Anselmo Kamada and Nicholas Parrish, all at RIKEN IMS, have investigated virus-derived variations in 3,332 people from diverse populations using bioinformatic tools specially designed for the task.
They discovered that viruses are responsible for unexpected structural variations in the human genome. They also found rare variants in the germline that can be traced back to human herpesvirus 6 (Fig. 1).
Not all the viral genetic material they found had ancient origins, however. The trio discovered that some commonly used cell lines had been infected by viruses. “We think these sequences are likely caused by infection of the subject who donated their blood for human genetics research,” says Parrish. “Strangely, the viruses don’t usually infect B cells, which were used to make the cell lines we used, and so we don’t fully understand how those viruses infected the cells.”
The team intends to explore the possible functions of the sequences they have identified. Some studies have suggested associations between viral genetic sequences and a higher risk of certain diseases, Parrish notes. “If that’s true, how and why are they maintained in the human population?” he asks. “We want to see if they provide some benefit in addition to the cost.”
Related contents
- Is there a bit of virus in our genome?
- A genome-wide knockout screen reveals genes needed for retroviral element silencing
Reference
- 1. Kojima, S., Kamada, A. J. & Parrish, N. F. Virus-derived variation in diverse human genomes. PLoS Genetics 17, e1009324 (2021). doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009324
