Aug. 1, 2024 Research Highlight Biology
Silencing the silencers in the hippocampus
By turning off neurons in one region of the hippocampus, researchers have shown the role they play in regulating oscillations
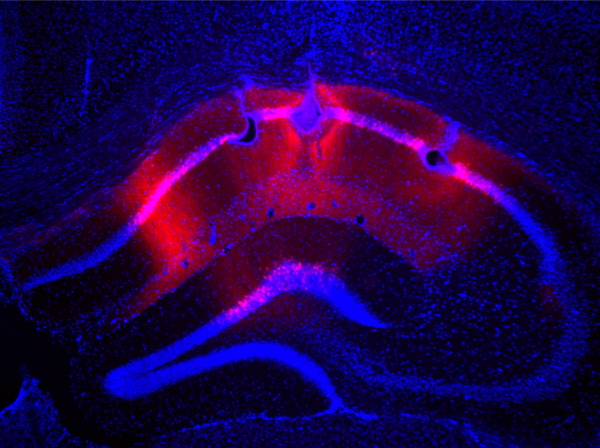
Figure 1: A fluorescence micrograph of a CA1 in a mouse’s hippocampus. RIKEN researchers silenced the pyramidal cells in this region. Reproduced from Ref. 1 and licensed under CC BY 4.0. © 2024 C. Adaikkan et al.
RIKEN neuroscientists have gained new insights into how the hippocampus generates and sustains oscillations, which will be helpful for informing models on how the brain region works1.
Thomas McHugh of the RIKEN Center for Brain Science has devoted most of his career to studying a single brain region—the hippocampus. One of the most studied regions in the mammalian brain, the hippocampus manages episodic memories and spatial navigation among other things. You use it when recounting events and locating your car in a parking lot.
“If you damage your hippocampus, you will lose the ability to form episodic memories, while retaining other kinds of memories such as motor memory,” explains McHugh. “That means, for example, you could still get better at tennis, but you won’t ever remember practicing.”
While the hippocampus has been much studied, many aspects of it remain mysterious. For example, waves of different frequencies flow through it, which perform different but overlapping functions. These oscillations are set up and sustained by precise timing of excitations and inhibitions, which are controlled by a delicate feedback mechanism. But to date no one has successfully modeled this process.
There are three such oscillations in the CA1 region of the hippocampus—a region towards the back end in terms of processing sensory input. Ripples are the fastest of these oscillations, with about 100 to 300 ripple oscillations per second.
Now, McHugh and co-workers have conducted a try-it-and-see experiment to discover what would happen if they turned off the output from pyramidal cells in the CA1 of mice by using a genetics approach (Fig. 1).
“We didn’t have a strong hypothesis,” recalls McHugh. “We knew things might look strange, but we didn’t really know what to expect.”
While the mice behaved similarly to normal mice, the thing that really stood out was the activity of their ripples. “Even when we were collecting the first data, it was obvious the ripples were very different—they were way larger and faster,” says McHugh. “It looked almost epileptic; there was this crazy activity all the time.”
McHugh suspects that this is because that CA1 pyramidal cells play an inhibitory role in regulating oscillations, and when this was turned off the oscillations went out of control.
“It’s like if you’re teaching a classroom and all the kids are screaming. If you’re trying to hear what one kid’s saying, you yell ‘Shut up!’ and let that kid talk,” says McHugh. “And so these neurons in the CA1 are basically telling all their neighbors to shut up through this inhibitory system.”
This finding will be invaluable for developing better models for the processing going on in the hippocampus.

Thomas McHugh (second row, fifth from right) and his team have silenced output from CA1 pyramidal cells in the mouse hippocampus to reveal their role in inhibiting oscillations.© 2024 RIKEN
Related content
- How the hippocampus orchestrates memory consolidation
- How left and right hippocampal CA1 regions in the mouse brain talk with each other
- Memory impairment in Down syndrome linked to inhibition in the hippocampus
Rate this article
Reference
- 1. Adaikkan, C., Joseph, J., Foustoukos, G., Wang, J., Polygalov, D., Boehringer, R., Middleton, S. J., Huang, A. J. Y., Tsai, L.-H. & McHugh, T. J. Silencing CA1 pyramidal cells output reveals the role of feedback inhibition in hippocampal oscillations.Nature Communications 15, 2190 (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46478-3
